Low-Cobalt Precursors Market to Reach USD 8,300.0 million by 2036 on 10% CAGR, Driven by EV Demand
Global low-cobalt precursors market forecast to grow USD 8,300.0 million by 2036 as EV adoption and battery innovation accelerate.
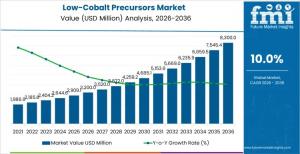
NEWARK, DE, UNITED STATES, January 19, 2026 /EINPresswire.com/ -- The global low-cobalt precursors market is projected to grow from USD 3,200.0 million in 2026 to USD 8,300.0 million by 2036, expanding at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.0% over the forecast period. The market’s growth is being shaped by accelerating electric vehicle (EV) adoption, rising pressure to reduce cobalt dependence, and sustained investment in advanced battery materials manufacturing.
Low-cobalt precursors are engineered intermediate materials used in the production of lithium-ion battery cathodes. They enable the development of nickel-rich chemistries such as NMC 811 and NMC 955, which reduce cobalt content while maintaining energy density and safety standards. These materials are increasingly central to battery supply chains serving passenger EVs, commercial vehicles, and stationary energy storage systems.
Request For Sample Report | Customize Report |purchase Full Report - https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/sample/rep-gb-31537
Market Context: Why Low-Cobalt Precursors Matter Now
The market is emerging at a critical juncture for the battery industry. Cobalt supply remains highly concentrated, with approximately 70% of global production originating from the Democratic Republic of Congo. This concentration exposes automakers and battery manufacturers to geopolitical risk, ethical sourcing concerns, and price volatility.
Low-cobalt precursor technologies address these risks by lowering cobalt content in cathodes while preserving performance. Nickel-rich formulations such as NMC 811 (80% nickel, 10% manganese, 10% cobalt) and NMC 955 (90% nickel, 5% manganese, 5% cobalt) are gaining traction due to their cost advantages and higher energy densities. Together, these chemistries account for 38.0% of the total low-cobalt precursors market.
The transition requires advanced precursor manufacturing techniques, including tightly controlled co-precipitation processes, automated production systems, and real-time quality monitoring. As a result, precursor production is evolving from a commodity chemical process into a capital-intensive, high-precision materials engineering discipline.
Market Size, Growth Outlook, and Key Metrics
• Market Value (2026): USD 3,200.0 million
• Market Forecast Value (2036): USD 8,300.0 million
• Forecast CAGR (2026–2036): 10.0%
• Leading Application: Passenger EVs (64.0% market share)
• Dominant Supply Form: Hydroxide precursors (52.0% market share)
• Leading Producer Type: Integrated cathode producers (48.0% market share)
Passenger electric vehicles remain the primary demand driver, reflecting global automotive electrification targets and mass-market EV rollout plans. The segment’s scale requires consistent precursor quality across millions of battery cells, reinforcing the role of vertically integrated producers that can align precursor properties with in-house cathode manufacturing processes.
Technology Trends Reshaping Precursor Manufacturing
Advanced process control systems are transforming how low-cobalt precursors are produced. Modern facilities deploy distributed control systems, machine learning tools, and digital twin models to optimize reaction kinetics, particle morphology, and impurity control in real time.
Hydroxide precursors, which dominate supply form demand, are favored for their superior reactivity during lithiation and their ability to deliver uniform cathode particle structures. Their production requires precise pH management, controlled atmospheres, and high-purity filtration systems, particularly for automotive-grade applications.
At the same time, intellectual property constraints are shaping competitive dynamics. Extensive patent portfolios around NMC 811, NMC 955, synthesis routes, and dopant strategies create barriers to entry and favor larger companies with established legal and R&D capabilities. Many suppliers are responding by forming licensing agreements or pursuing alternative formulations that avoid patented pathways.
Regional Outlook: Growth Patterns Across Major Markets
The low-cobalt precursors market is expanding unevenly across regions, reflecting differences in battery manufacturing capacity, policy support, and raw material access.
• China (CAGR 11.2%) leads global growth, supported by large-scale investments from companies such as Huayou Cobalt, Zhejiang Huayou New Energy, and Ronbay Technology. Strong government backing for new energy vehicles and close integration across the battery supply chain underpin this expansion.
• Brazil (CAGR 10.8%) is emerging as a strategic hub, driven by domestic nickel reserves, expanding EV manufacturing, and policies promoting value-added mineral processing.
• United States (CAGR 9.9%) growth is being shaped by federal initiatives under the Inflation Reduction Act and CHIPS Act, aimed at building domestic battery supply chains and reducing reliance on foreign materials.
• United Kingdom (CAGR 9.7%) and Germany (CAGR 9.6%) are leveraging strong chemical engineering capabilities and sustainability-focused policies to advance precursor technologies aligned with European environmental standards.
• South Korea (CAGR 9.2%) benefits from its integrated battery ecosystem and export-oriented manufacturing strategy.
• Japan (CAGR 8.5%) continues to prioritize precision manufacturing and long-term R&D investments in premium precursor materials.
Competitive Landscape and Key Players
The market features a mix of global chemical groups, specialist materials suppliers, and vertically integrated battery manufacturers. Key companies include:
• Umicore
• BASF
• POSCO Future M
• Huayou Cobalt
• Zhejiang Huayou New Energy
• Ronbay Technology
• LG Chem
• ECOPRO BM
Manufacturers are securing market share by demonstrating consistent precursor performance in real cathode production, scaling capacity reliably, and maintaining close technical alignment with evolving cell designs. Investment in pilot lines, advanced characterization tools, and regional supply support is becoming a competitive necessity.
Outlook: What Comes Next
From 2026 to 2036, the low-cobalt precursors market is expected to remain a strategic growth segment within the broader battery materials industry. Continued reductions in cobalt content, rising demand for high-nickel chemistries, and stricter sustainability requirements are likely to drive further innovation in precursor formulations and manufacturing processes.
As battery supply chains mature, companies that can combine secure raw material sourcing, advanced process control, and compliance with automotive-grade standards are positioned to play a central role in the next decade of electrification.
Browse Related Insights
Ultra-high Molecular Weight Polyethylene Market Share Analysis: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/ultra-high-molecular-weight-polyethylene-market-share-analysis
Chlorotoluene Market Share Analysis: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/chlorotoluene-market-share-analysis
Germany Refinery Catalyst Market: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/germany-refinery-catalyst-market
Japan Refinery Catalyst Market: https://www.futuremarketinsights.com/reports/japan-refinery-catalyst-market
About Future Market Insights (FMI)
Future Market Insights, Inc. (FMI) is an ESOMAR-certified, ISO 9001:2015 market research and consulting organization, trusted by Fortune 500 clients and global enterprises. With operations in the U.S., UK, India, and Dubai, FMI provides data-backed insights and strategic intelligence across 30+ industries and 1200 markets worldwide.
Sudip Saha
Future Market Insights Inc.
+1 347-918-3531
email us here
Legal Disclaimer:
EIN Presswire provides this news content "as is" without warranty of any kind. We do not accept any responsibility or liability for the accuracy, content, images, videos, licenses, completeness, legality, or reliability of the information contained in this article. If you have any complaints or copyright issues related to this article, kindly contact the author above.